Greenhouse Effect Global warming describes the current rise in the average temperature of Earth's air and oceans Global warming is often described as the most recent example of climate change Grades 11, 12 Subjects Earth Science, Meteorology, Geography Contents 6 ImagesAlso methane, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) Possible implications of increased greenhouse effect Junior Cycle Science Earth and space Sustainability 3My calculations of CFC greenhouse effect show that there was global warming by about 06 °C from 1950 to 02, but the earth has actually cooled since 02 The cooling trend is set to continue

2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram
Global warming greenhouse effect diagram drawing
Global warming greenhouse effect diagram drawing-The greenhouse effect and the influence of human activity on it Greenhouse gases and their relative effects especially carbon dioxide and water vapour;Image result for poster on global warming drawing for kids Image result for poster on global warming drawing for kids Today Explore When autocomplete results are available use up and down arrows to review and enter to select Touch device users, explore by touch or with swipe gestures




Drawing Of Greenhouse With Glass Walls And Roof Plants Growing Inside Sunlight Coming In Through Roof But B Greenhouse Effect Green House Effect Greenhouse
018 °C during the 100 years ending in 05The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)The greenhouse effect is HUGE !The Earth's natural greenhouse effect and account for about 90% of the total heatretaining capacity of the atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface, trapping the heat in our atmosphere instead of letting it escape to space The Greenhouse Effect is a natural process essential
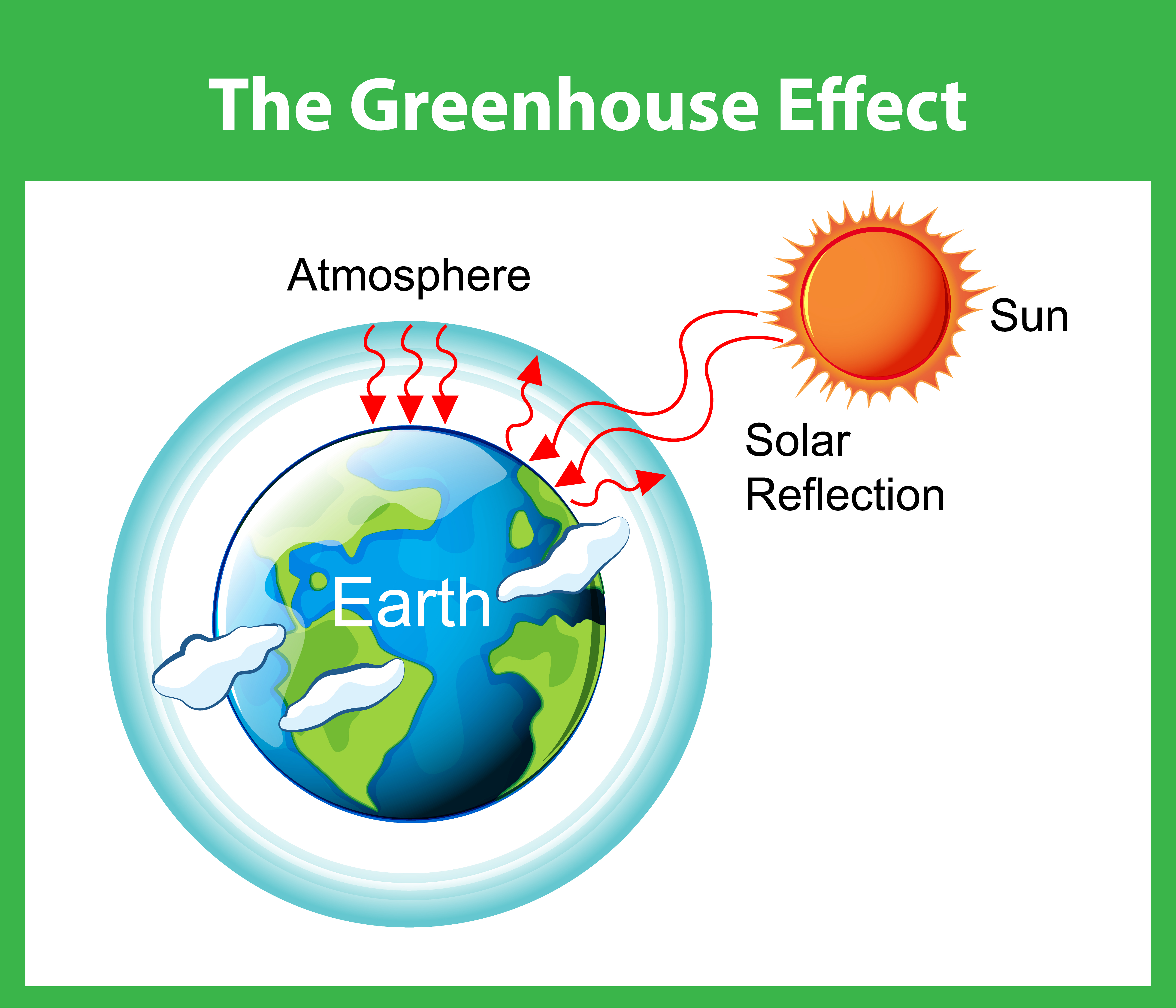
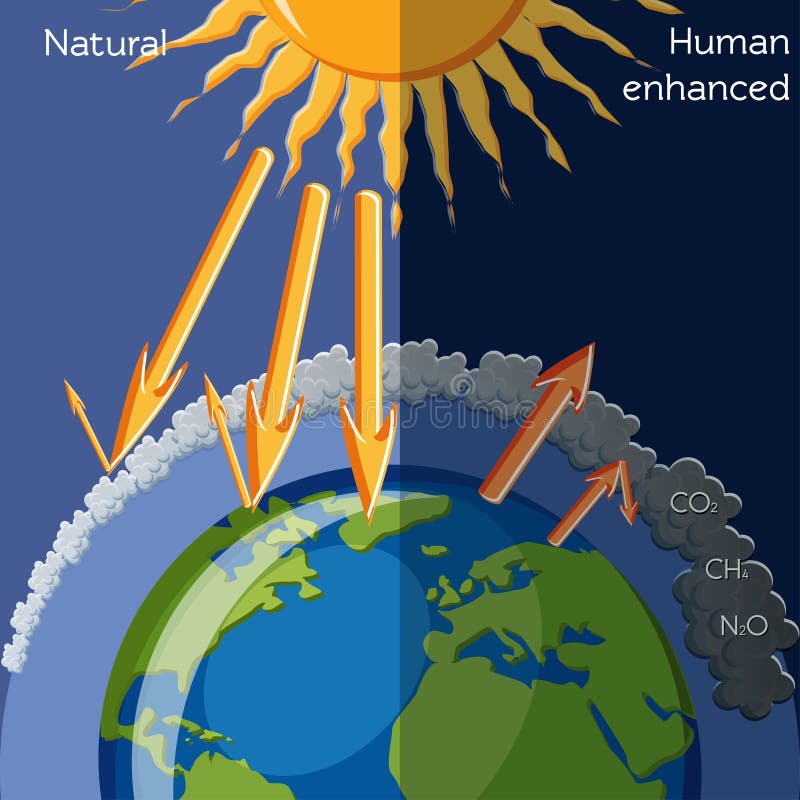
The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxidesGlobal warming is the increase in the average measured temperature of the Earth's nearsurface air and oceans since the midth century, and its projected continuation In media, it is synomonous with the term climate change Global surface temperature increased 074 ±Thankfully, greenhouse gases also save the day!
Or is such thinking a myth brought about by flawed or incomplete science?Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16°About half of that energy goes out into space, and about half of it returns to Earth as heat, contributing to the 'greenhouse effect' By measuring the wavelengths of infrared radiation that reaches the surface, scientists know that carbon dioxide, ozone, and methane are significantly contributing to rising global temperatures




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube



The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download
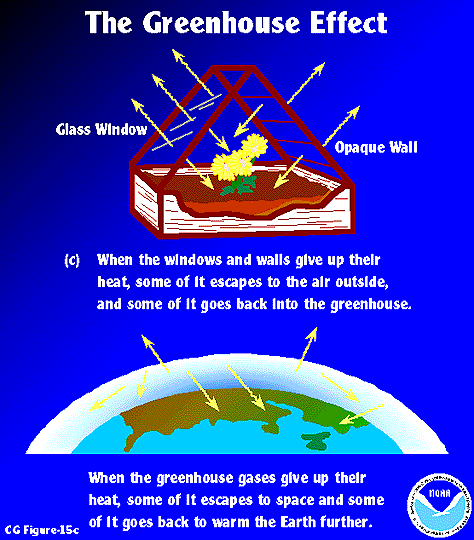
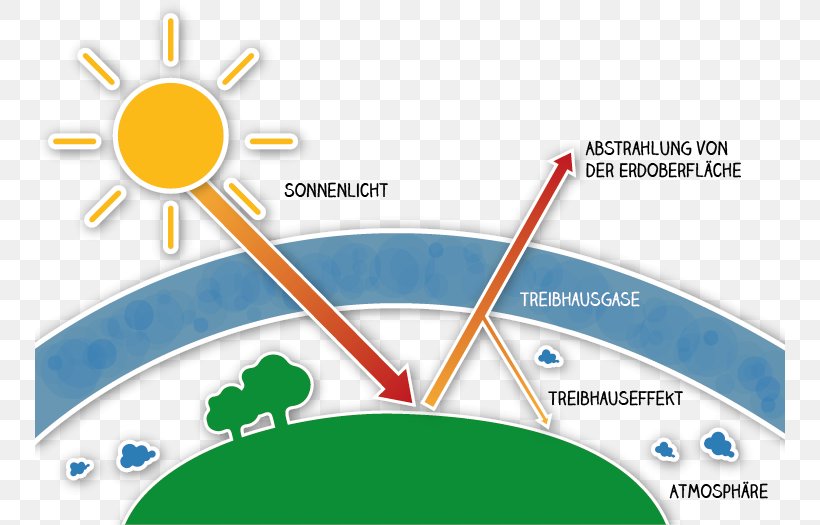
The past decade has been the hottest ever recorded since global temperature records began 150 years ago This video discusses the impacts of the sun's energy, Earth's reflectance and greenhouse gasses on global warmingThe diagram outlines how the greenhouse effect works Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere The ground warms up and heat is emitted from the Earth's surface Some heat escapes into spaceF) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearly




Global Greenhouse Gases Emission And Their Characteristics Greenhouse Effect The Largest Emitting Countries Carbon Dioxide Canstock




Greenhouse Effect Vs Global Warming Drawing Easy Drawing For Kids Youtube
Furthermore, if this were linear then we would get 1°C increase for every 7 W/m2 Thankfully this is not the case, but adding more greenhouse gasesThe Greenhouse Effect Task Easy Draw a labeled diagram to model your teacher's description of the greenhouse effect Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere and warms the Earth's surface The heat is radiated back towards space Most of the outgoing heat is absorbed/trapped by greenhouse gas molecules in the Earth's atmosphereThe 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect




The Greenhouse Effect Explained



Climate Change And Global Warming Introduction Global Issues
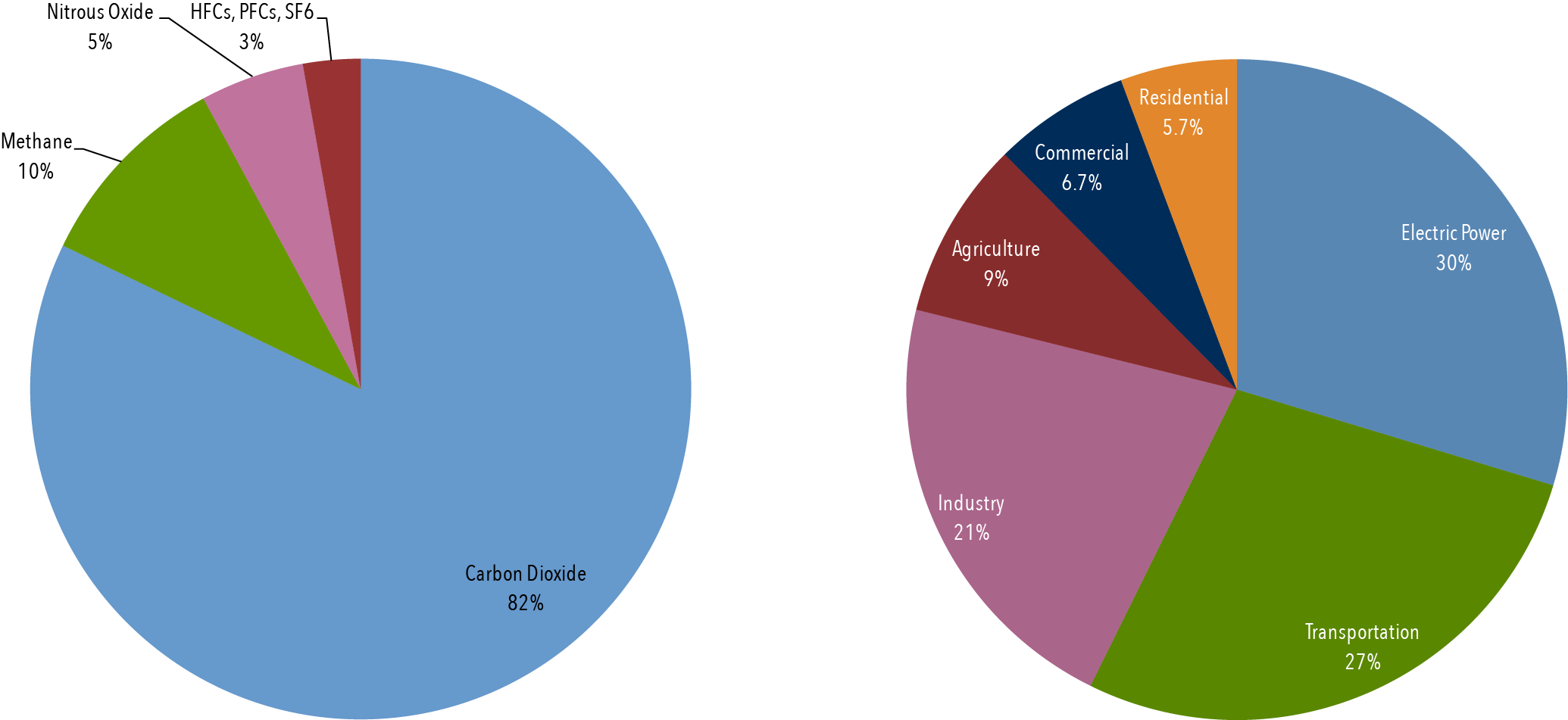
An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percent Top ofThere is NO net warming effect due to socalled greenhouse gases That being said, here's what I'm NOT sayingI'm not saying global warming isn't real We are experiencing a warming trendI'm not saying human activity doesn't add to this warming trend;The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect Are global cooling gasses while nitrous oxide (n2o) is a greenhouse gas The greenhouse effect human activities contribute to global warming by increasing the greenhouse effect O earth's net heat has no effect on the oceans




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
The greenhouse effect and global warming 3 Analyze global warming diagrams and resources to obtain a clear understanding of this scientific process 4 Hypothesize about the effects of global warming on the climate and the world's populations 5 Conduct research using a variety of primary sources to explore perspectives in the global warmingGreenhouse gases slow down the rate of heatloss from the surface of the Earth, like a blanket that slows down the rate at which your body loses heat The result is the same in both cases, the surface of the Earth, or of your body, gets warmer So global warming does not violate the second law of thermodynamicsUse the back of this worksheet if necessary




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature
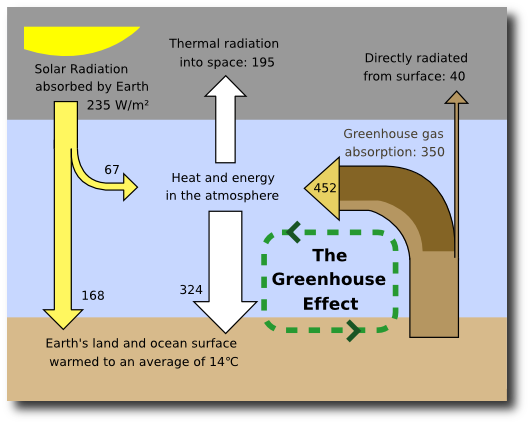
Yes While we cannot stop global warming overnight, or even over the next several decades, we can slow the rate and limit the amount of global warming by reducing human emissions of heattrapping gases and soot ("black carbon") If all human emissions of heattrapping gases were to stop today, Earth's temperature would continue to riseThe uncertainty lies in the magnitude of the responseIt is well established that the global mean surface temperature of the Earth has increased over the past century by about 06 K4 Global Warming A Science Overview The Potential Impacts of Climate Change on Transportation Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the Earth's greenhouse effect, with arrows proportional in size to the fluxes of energy by the particular process (NAST, 00) Of incoming solar radiation, about 30% is reflected back into space




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram



Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Png Clipart Brand Circle Diagram Drawing Encapsulated Postscript Free Png Download
Global Warming is the increase in global temperatures due to the increased rate of the Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse gases trap the incoming solar radiation, these gases include Carbon Dioxide, CFCs, Methane, Nitrous Oxides and other Halocarbons These are released by human activity We need the Greenhouse effect to maintain life on earth as we know ithowever if we keep adding to the GreenhouseGreenhouse effect and Global Warming A greenhouse is a structure whose roof and walls are made chiefly of transparent material, such as glass, in which plants requiring regulated climatic conditions are grown In a greenhouse, the incident solar radiationGlobal warming global warming Feedback mechanisms and climate sensitivity There are a number of feedback processes important to Earth's climate system and, in particular, its response to external radiative forcing The most fundamental of these feedback mechanisms involves the loss of longwave radiation to space from the surface Since this radiative loss increases with




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect
F) between 1906 and 05, and the rate of temperature increase has nearlyGlobal warming causes 300,000 deaths a year Likewise, according to research published in Nature, by 50, rising temperatures could lead to the extinction of more than a million species And because we can‟t exist without a diverse population of species on Earth, this isEnergy resources diagram Consumption of energy resources, (eg turning on a light) requires resources and has an effect on the environment Many electric power plants burn coal, oil or natural gas in order to generate electricity for energy needs While burning these fossil fuels produces a readily available and instantaneous supply of




How Should Climate Change Be Taught In Schools Across America Ensia



The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Vector Art At Vecteezy
Additional warming is commonly referred to as Greenhouse Warming Greenhouse Warming is global warming due to increases in atmospheric greenhouse gases (eg, carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, etc), whereas Global Warming refers only to the observation that the Earth is warming, without anyThe Carbon Cycle, Greenhouse Effect &The greenhouse effect of Venus From geometry, we can calculate the average solar flux over the surface of Venus It is approximately 661 W/m2 Venus is very reflective of solar radiation In fact, it has a reflectivity (or albedo) of 08, so the planet absorbs approximately 661 X 02 = 132 W/m2 By assuming that the incoming radiation equals the



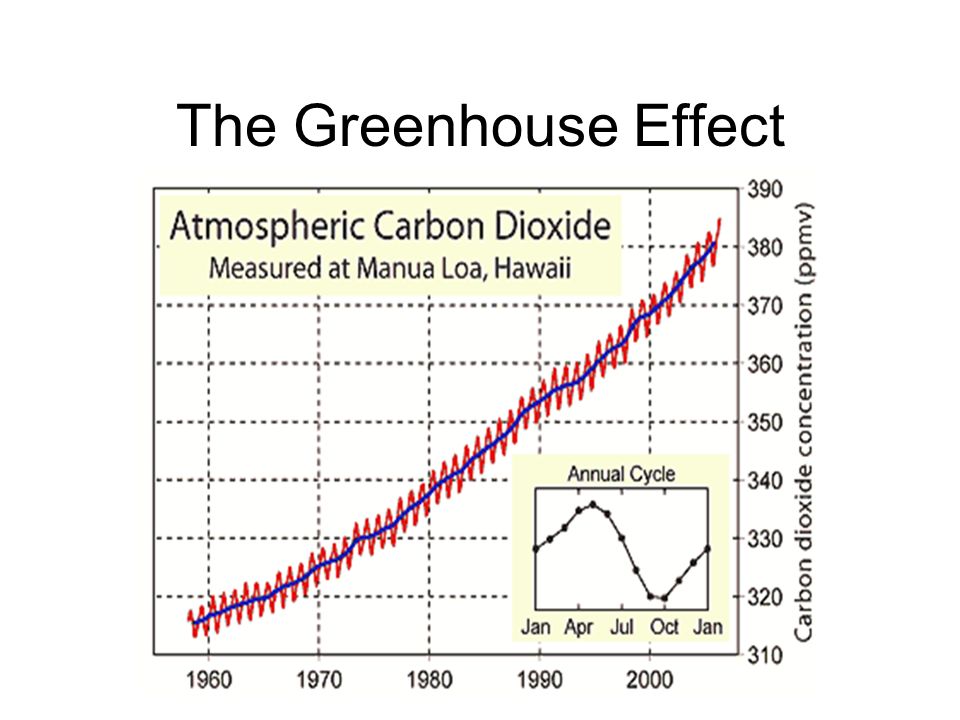
Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
Venus may have had a shallow liquidwater ocean and habitable surface temperatures for up to 2 billion years of its early history, according to computer modeling of the planet's ancient climate by scientists at NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in247 greenhouse effect diagram stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse effect diagram stock video clips of 3 global warming, sun earth diagram energy global problems effects global warming greenhouse effect global waste management greenhouse effect vector global warming icons greenhouse gas effectFrom the "no atmosphere" model of 18°C to an observed average surface temp of 15°C, it is a 33°C effect !




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
The greenhouse effect on the planet Venus is _____ the greenhouse effect on the planet Earth (a) stronger than (b) weaker than 4 Since 1860, the 11 warmest years in terms of the measured global average surface temperature have occurred since 1990FIG 417 Student drawn computer diagram of the greenhouse effect Solar radiation is emitted from the sun, headed toward Earth Most of the sun's radiation is absorbed by the earth's surface, thus warming the earth Some of the solar radiation is reflected back out to space by the earth surface and atmosphereIs human activity causing alarming global warming scenarios and related catastrophes?




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
Global Warming Fact or Fiction?Figure 71 Rise in the concentrations of greenhouse gases since the 18th century As we will see in section 73, simple theory shows that a rise in greenhouse gases should result in surface warming;Research has also provided evidence that has led to refinements of the hypothesis about the causes of global warming For example, current evidence supports the more inclusive hypothesis that global warming has been caused by increases in several greenhouse gases, including primarily CO 2, nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and methane (CH 4)




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



The Greenhouse Effect
Surrounding the greenhouse effect and global warming Here's how you can help Task 1 Draw a diagram illustrating the greenhouse effect Label it carefully Task 2 Below your diagram write a concise paragraph that explains the diagram Write neatly and use correct English!The Short Answer The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes Earth a comfortable place to liveGlobal warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earth's average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released as people burn fossil fuels The global average surface temperature rose 06 to 09 degrees Celsius (11 to 16°



Climate Change Education Stock Illustrations 526 Climate Change Education Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students
Have students create a diagram depicting the Greenhouse Effect using paper, markers, etc Tell them that they will be asked to go home and explain the Greenhouse Effect and global warming to a family member using their diagram as part of a homework assignment Have them practice presenting global warming using their diagrams with peer partnersThe greenhouse effect is a process by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric greenhouse gases, and is reradiated in all directions Since part of this reradiation is back towards the surface and the lower atmosphere, it results in an elevation of the average surface temperatureGreenhouse effect that is a direct result of human activities, unless natural causes can be identified and subtracted from the present warming trend Figure 1 From the top, the basic data on global warming the IPCC interpretation (indicating that the 06°C increase is caused by the greenhouse effect), another interpretation, suggesting a




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Cyberphysics Global Warming
Finding the answers to these questions has turned global warming into a highly politicized and contentious issueThe Greenhouse Effect Goal Students will learn how greenhouse gases temporarily trap heat within Earth's atmosphere, warming our planet via the greenhouse effect Activity Students explore the greenhouse effect through computer simulations and then dive deeper learning how the greenhouse effect works via readings and videos onlineThese characteristics are incorporated in the Global Warming Potential (GWP), a measure of the radiative effect (ie the strength of their greenhouse effect) of each unit of gas (by weight) over a specified period of time, expressed relative to the radiative effect of carbon dioxide (CO 2) This is often calculated over 100 years, though it




What Is Greenhouse Effect Definition Causes And Effects



Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Greenhouse Gas Anthropogen Global Warming Png 750x525px Greenhouse Effect Area Atmosphere Of
It doesI'm not saying trying to minimize environmental impact isn'tBuild a simple model to recreate the greenhouse effect Record observations of global warming during experiments Compare their model environment with their environment Describe how global warming may impact an engineer's decisions, their own lives and the Earth Discuss their roles as citizens in the reduction of greenhouse gasesEnergy resources diagram Consumption of energy resources, (eg turning on a light) requires resources and has an effect on the environment Many electric power plants burn coal, oil or natural gas in order to generate electricity for energy needs While burning these fossil fuels produces a readily available and instantaneous supply of




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect is the warming that happens when certain gases in Earth's atmosphere trap heat These gases let in light but keep heat from escaping, like the glass walls of a greenhouse



A Questions And Answers About Greenhouse Warming Policy Implications Of Greenhouse Warming Mitigation Adaptation And The Science Base The National Academies Press




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Kidminds
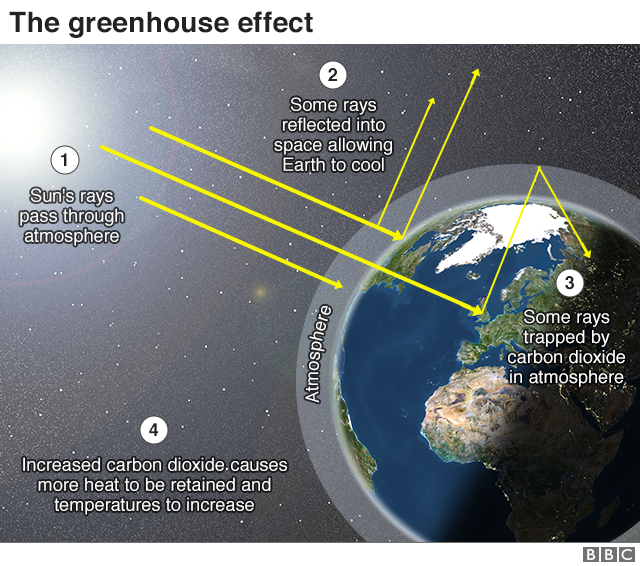



What Is Climate Change A Really Simple Guide c News




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Best Greenhouse Effect Ideas Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse What Is A Conservatory
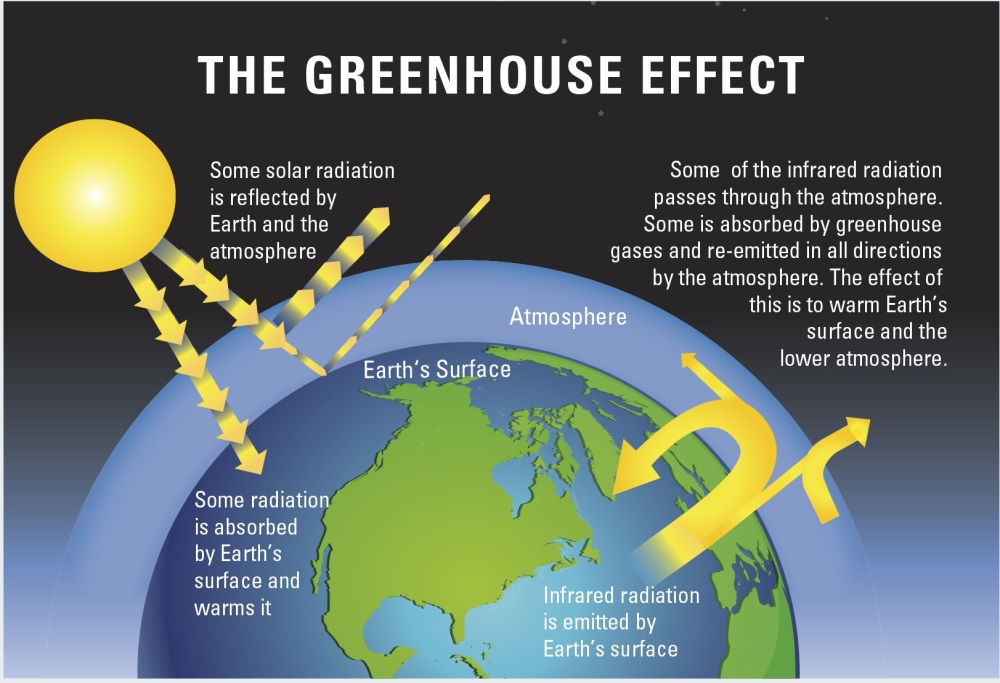



What Is The Relationship Between Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Socratic
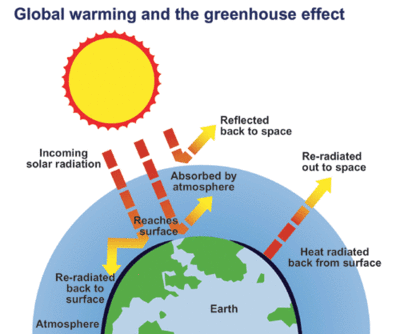



Climatechange Common Cops




Name Global Climate Change Webquest Greenhouse Effect Go To




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
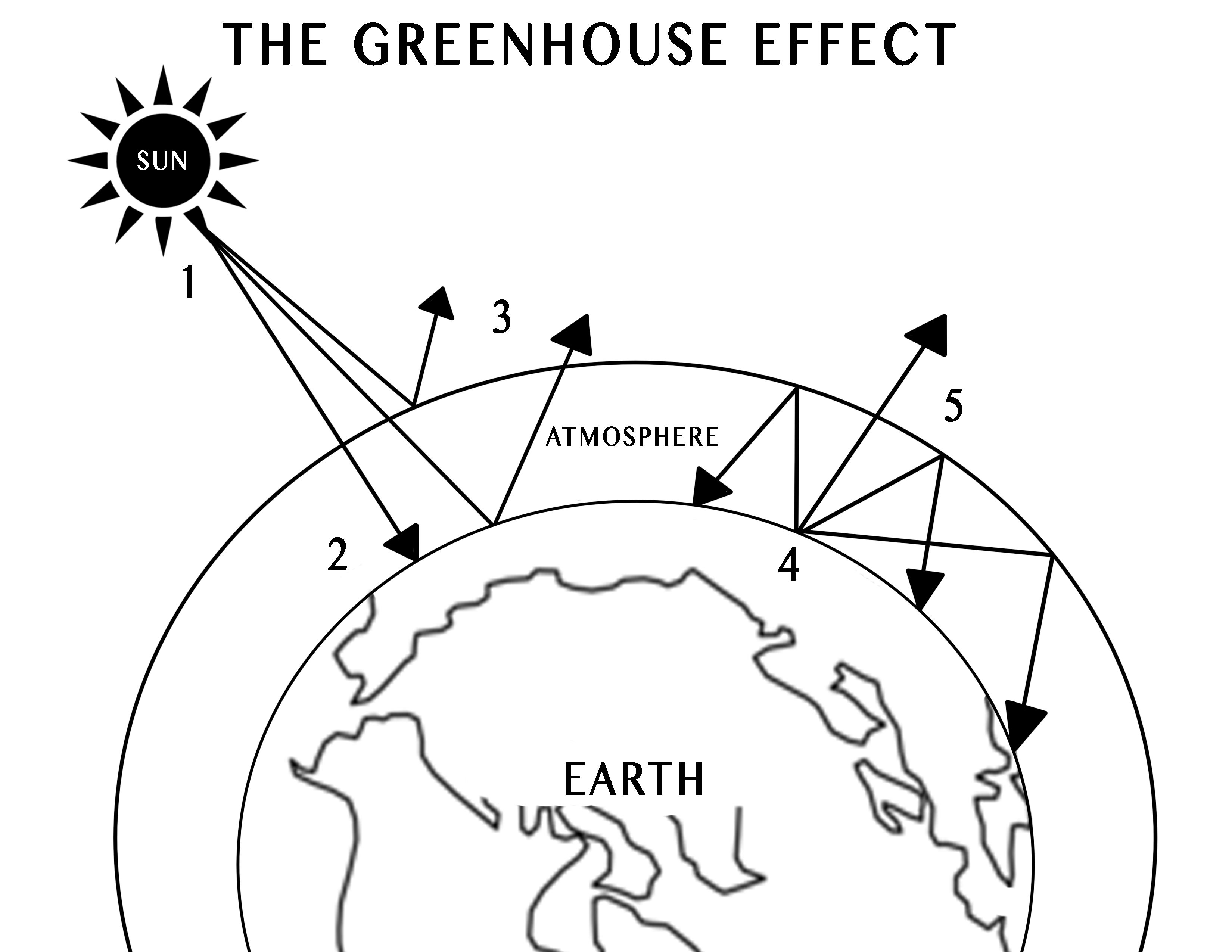



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng




Example Of Student Drawing Based On Textbook Diagram Download Scientific Diagram



How Deforestation Contributes To The Greenhouse Effect
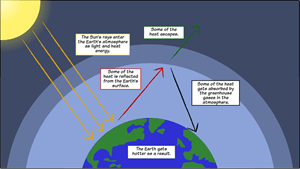



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




4 2 The Greenhouse Effect A Biology




Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




Teaching Climate Change American Federation Of Teachers




Greenhouse Effect High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature
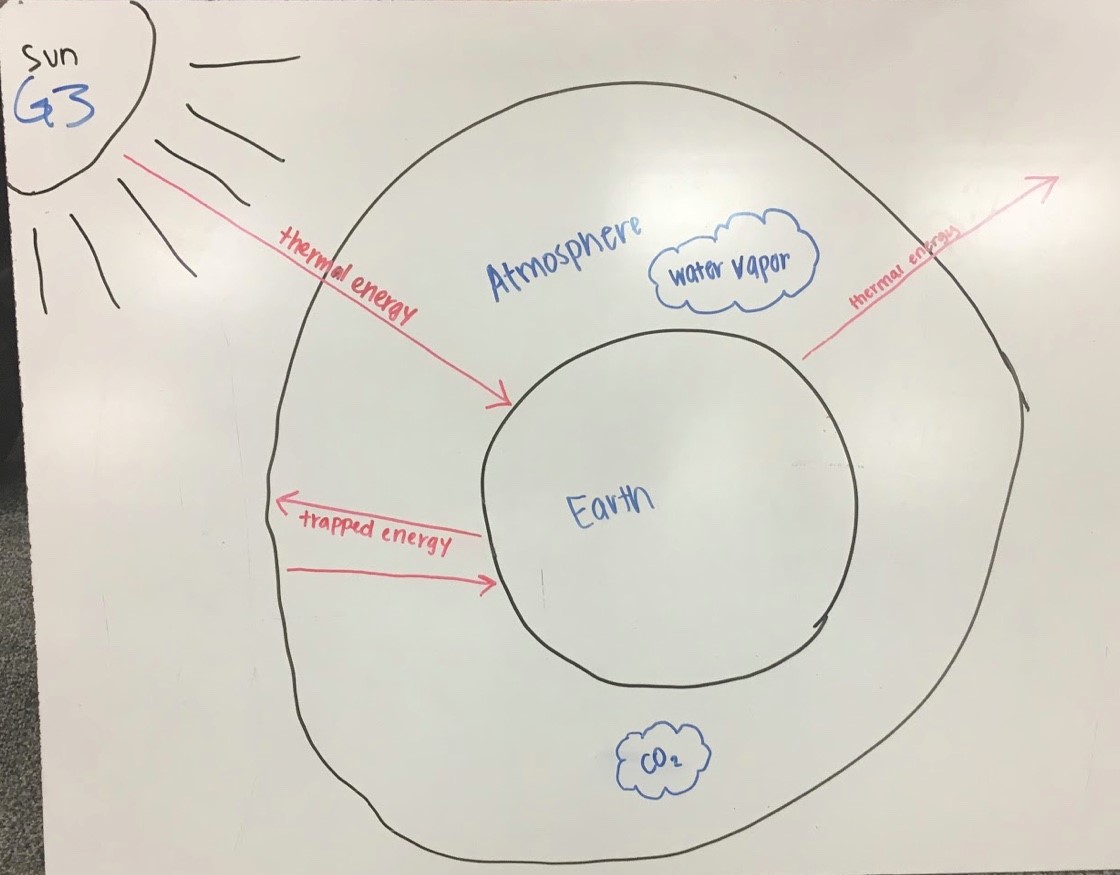



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena
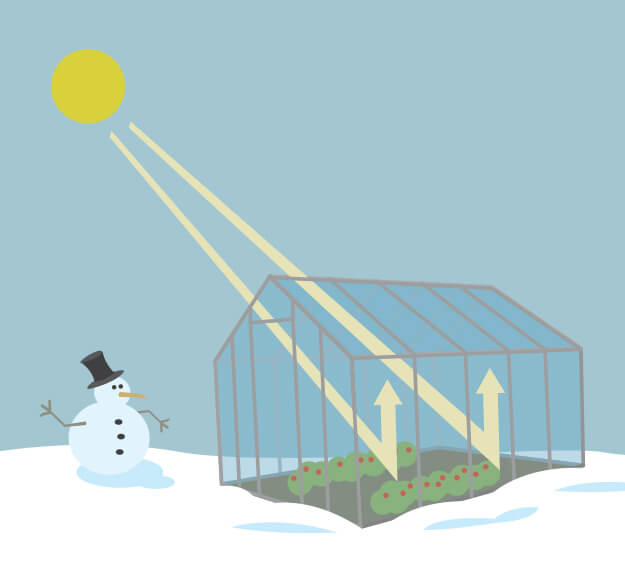




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top
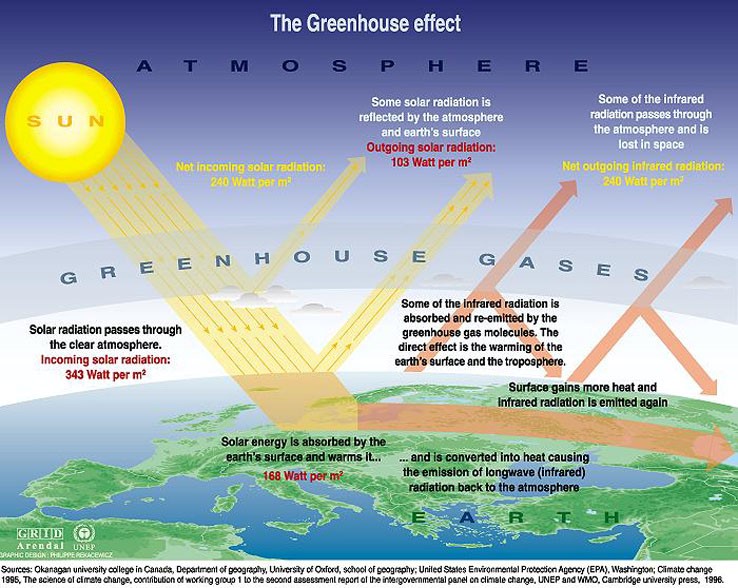



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




What Is A Conservatory What Is A Conservatory Global Warming Project Visible Light



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



2 2 1 Causes Of Global Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Drawing Easy Novocom Top
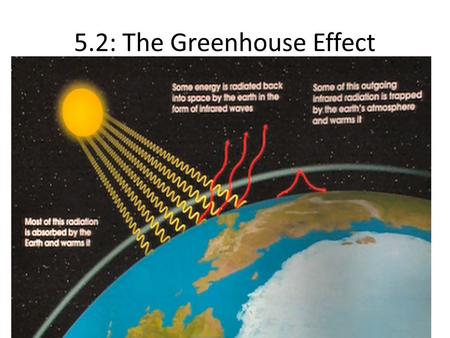



The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Concepts Videos And Examples




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
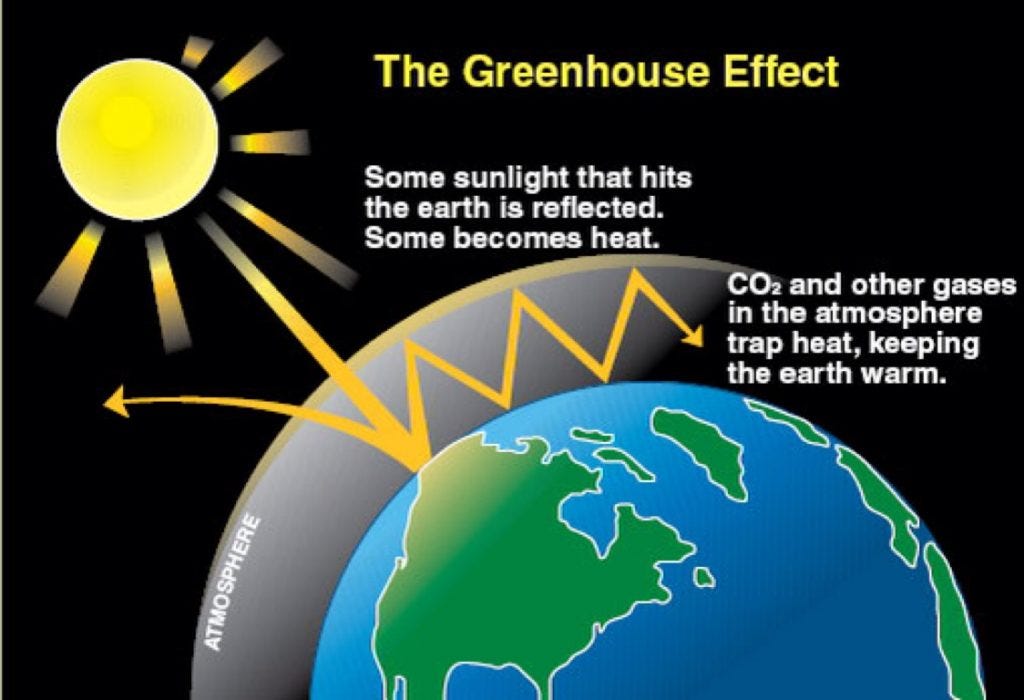



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Greenhouse Warming What Is It Reuben H Fleet Science Center
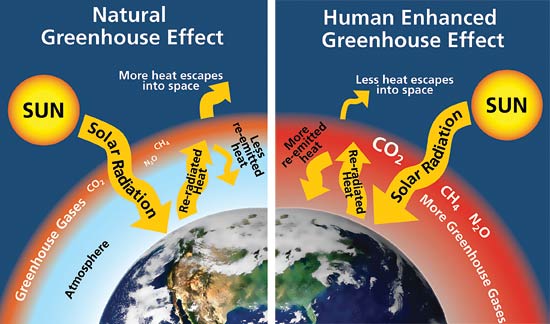



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
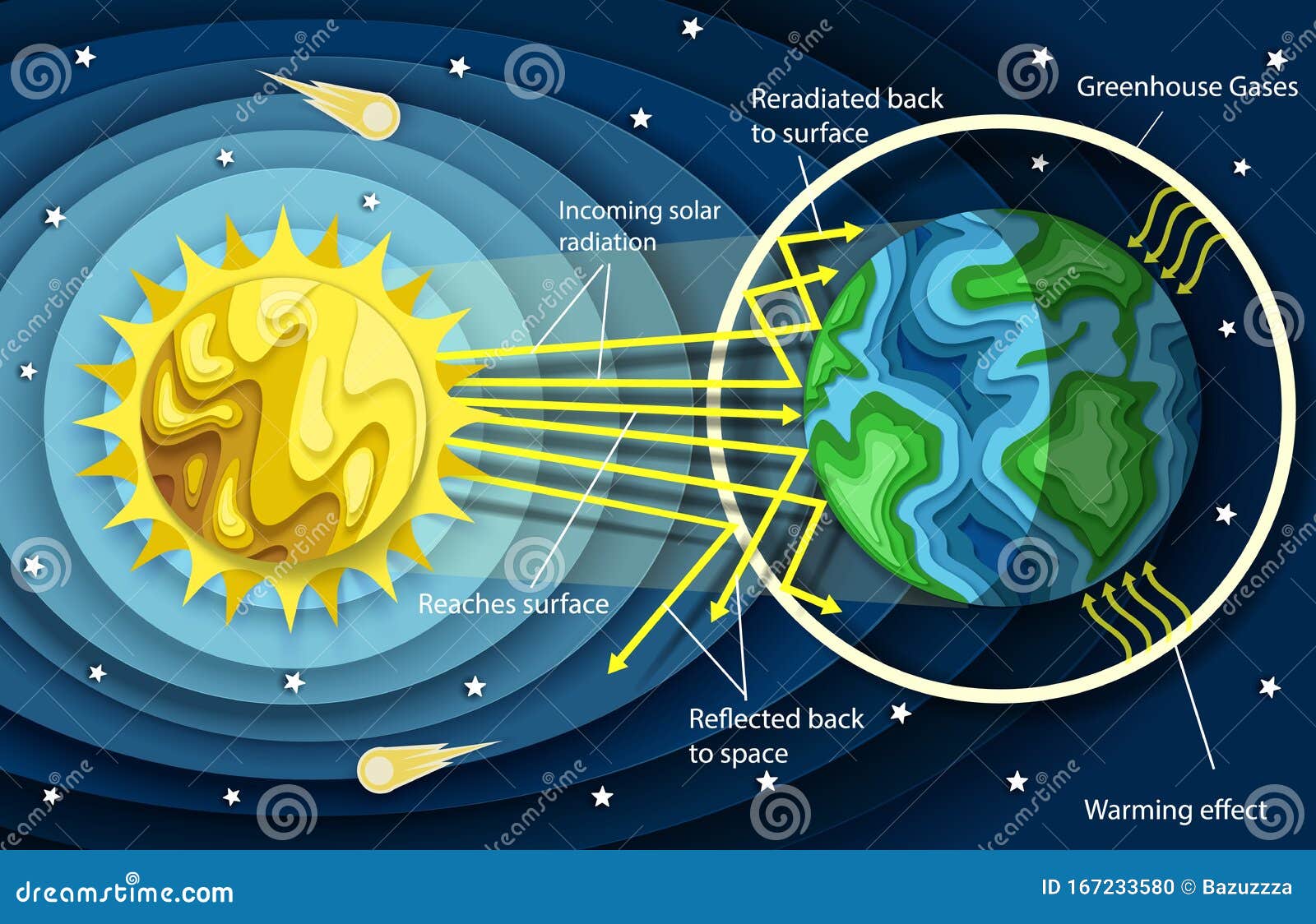



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




Drawing Of Greenhouse With Glass Walls And Roof Plants Growing Inside Sunlight Coming In Through Roof But B Greenhouse Effect Green House Effect Greenhouse




The Greenhouse Effect The Atmosphere Siyavula
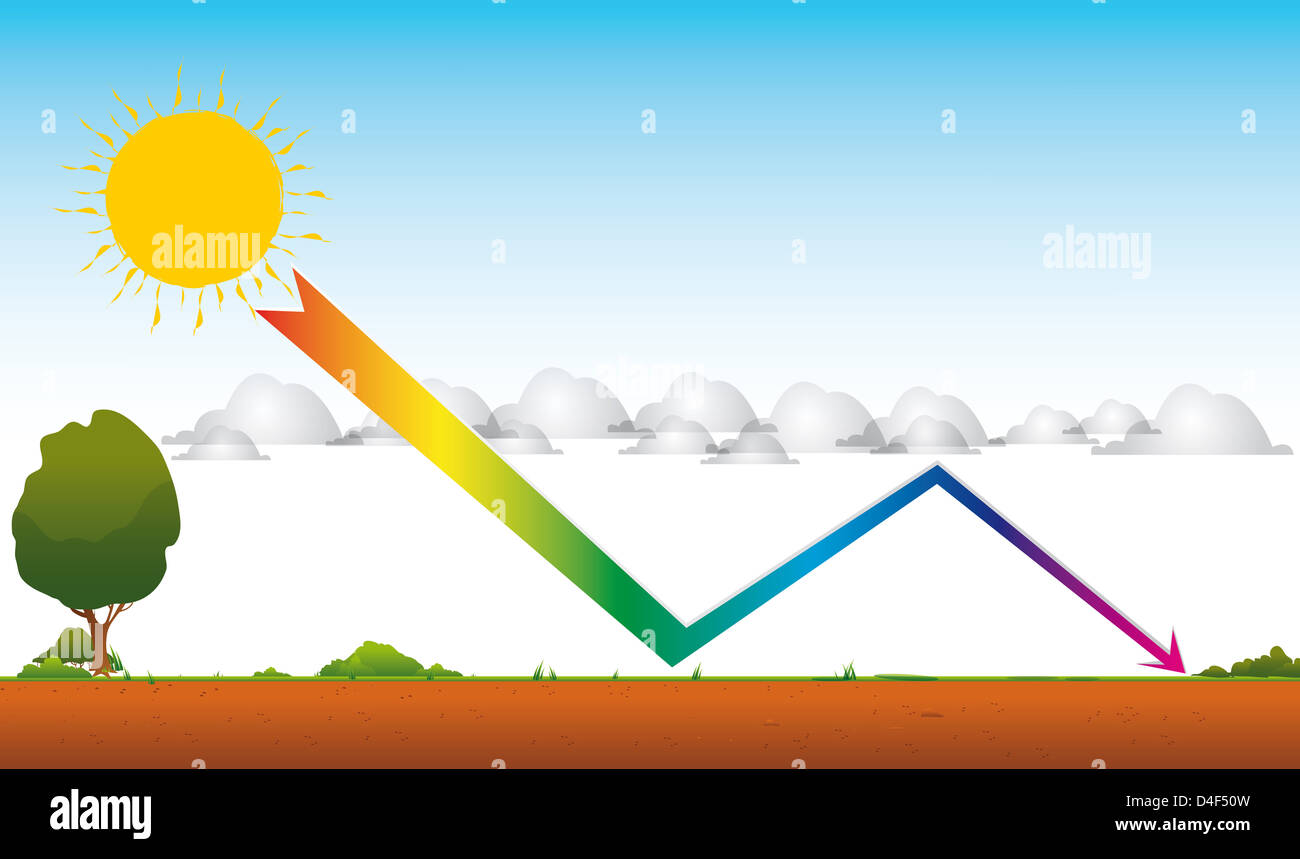




Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic



The Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect Apes By Reymond P
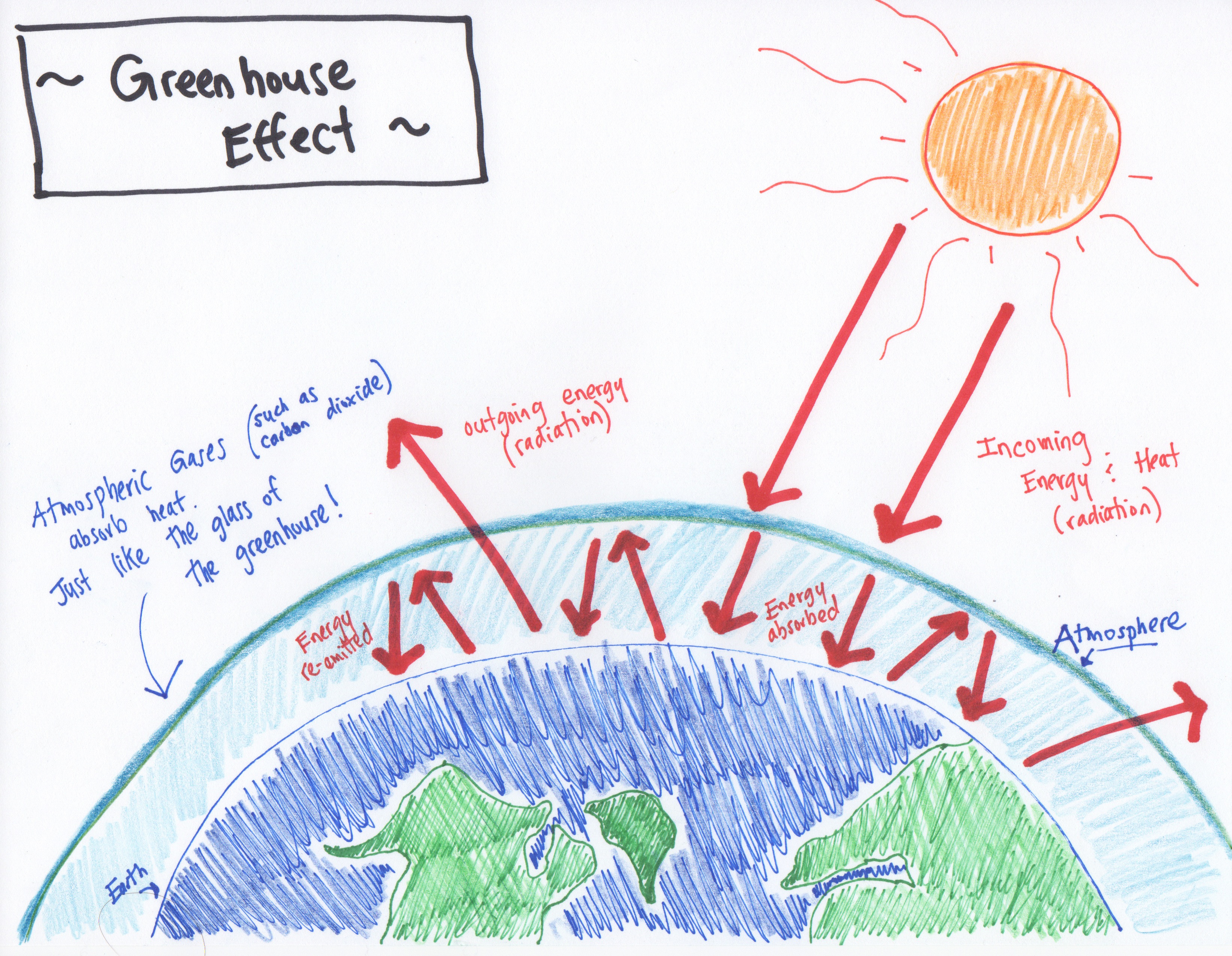



Climate Change Silence Is Ignorance Really Bliss Early Career Ecologists




Global Warming For Kids A Simple Explanation Of Climate Change
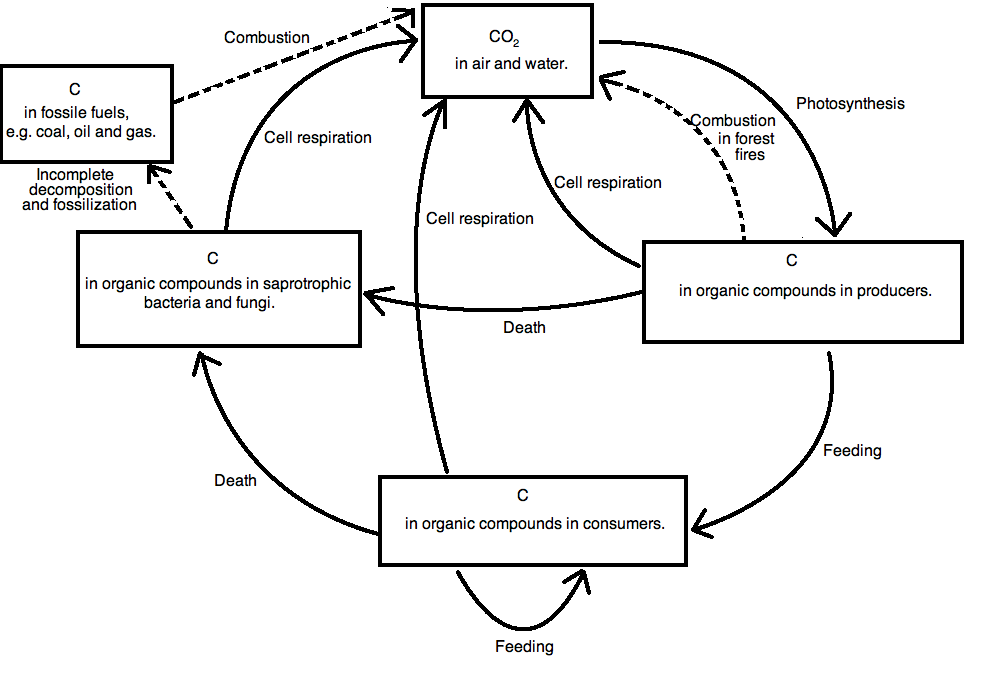



Ib Biology Notes 5 2 The Greenhouse Effect
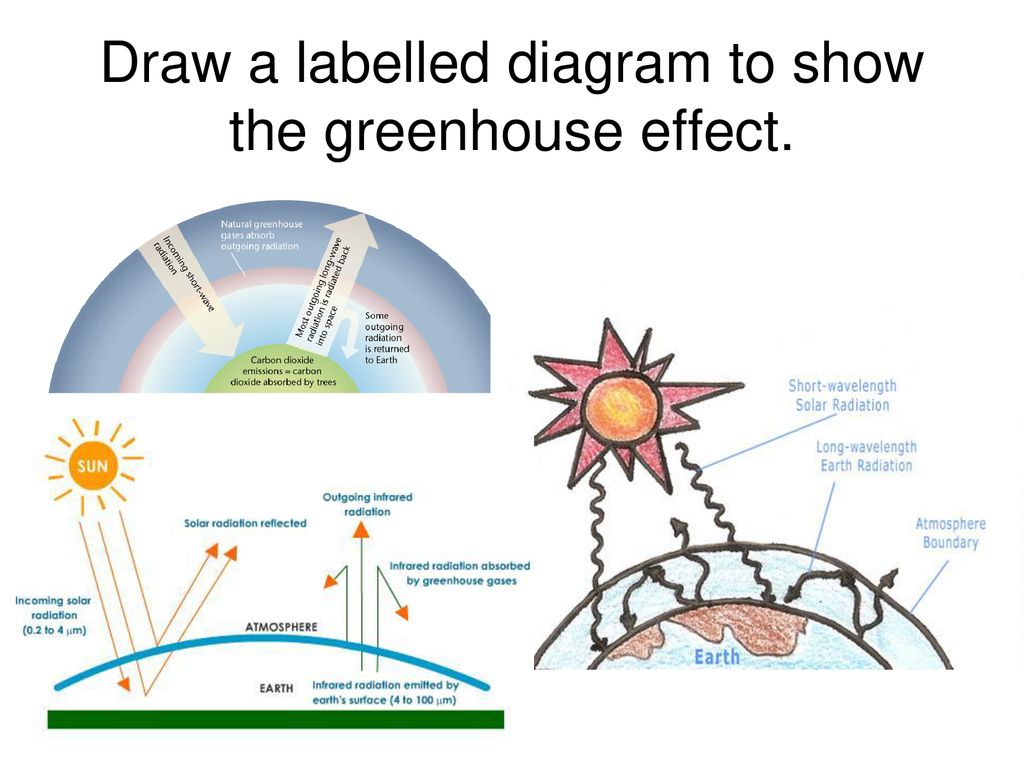



Lesson Ppt Download



Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Best Greenhouse Effect Ideas Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse What Is A Conservatory
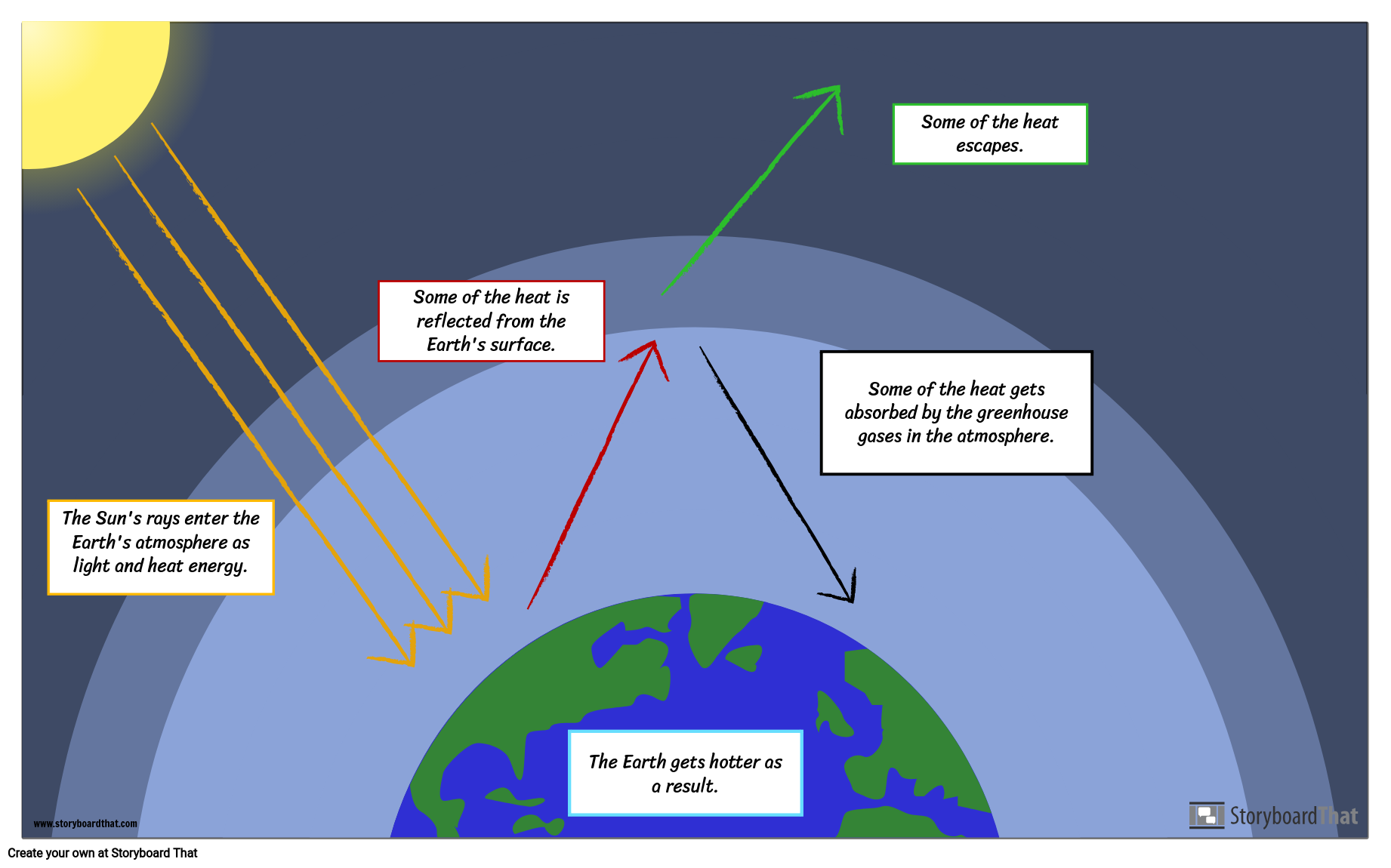



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Drawing Global Warming Greenhouse Effect High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram




Global Warming Definition Causes Effects Solutions Facts Britannica




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



1




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Q Tbn And9gcqh0jupg3p Zz6lfbc5xhscznxwfk4ldvqaetml Nqvnvmx8swv Usqp Cau



The Greenhouse Effect



1
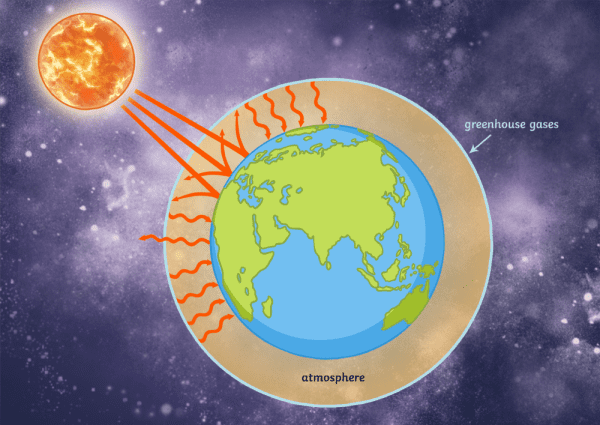



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top




Greenhouse Effect Aumsum Kids Science Education Children Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿